Essentials of Identity Security Posture Management
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) is a framework that continuously monitors, assesses, and improves the security of identity-related systems and access controls, ensuring that user identities, permissions, and access behaviors align with an organization's security policies. ISPM ensures that only the right users have the right access at the right time, reducing the likelihood of insider threats and enhancing overall compliance.
The importance of ISPM in today’s IT
ISPM’s comprehensive approach helps organizations proactively identify and mitigate identity-related security risks, such as over-privileged accounts, misconfigurations, and unauthorized access – all leading causes of data breaches in today’s cloud and hybrid environments.
ISPM brings together several key technologies working together to monitor, secure, and manage identities and their associated risks across cloud and on-premises environments. Using these tools together gives organizations a comprehensive way to ensure they maintain strong identity security postures on all fronts.
How ISPM works
ISPM encompasses a range of critical components designed to enhance an organization's overall identity security posture. Solutions under the ISPM umbrella include:
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA)
User Behavior Analytics (UBA)
Access and Entitlement Management
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)
Each capability plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the ISPM framework.
Access management within the ISPM framework, for example, focuses on the provisioning and control of user access across the organization's various systems and applications. Robust access controls ensure that only authorized users can interact with critical assets, reducing the risk of potential security incidents.
Identity governance in the ISPM context, meanwhile, ensures that user permissions align with an organization's policies and compliance requirements. It involves monitoring, certifying, and auditing access rights to prevent unauthorized access and eliminate policy and regulatory violations.
By integrating these and other identity-centric security capabilities, ISPM helps organizations streamline security operations, reduce their attack surface, and stay well-prepared to face an ever-evolving threat landscape.
The role of automation in ISPM
Automating core functions of ISPM lets organizations streamline and optimize processes for managing and monitoring privileges and access rights. Automating ISPM tasks – such as user provisioning, access requests, and policy enforcement – reduces the burden on IT and security teams while also minimizing the risk of human error.
Through automation, ISPM can quickly identify and respond to incidents like unauthorized access attempts or policy violations. Automated remediation processes can help contain and mitigate the impact of such incidents, keeping the organization's assets and data secure.
Overall, automation within an ISPM solution not only increases operational efficiency but also works to enhance the organization's identity security posture. Leveraging automation to manage and control identities, devices, and data, ISPM ensures a proactive and effective approach to identity-centric security management.
Where ISPM really shines: integration and scalability
Many organizations attempt to close the identity-security gap with multiple tools and systems, the complexity of which can lead to a lack of visibility and control. Taking a unified approach to identity security with ISPM reduces complexity and eases the monitoring, analysis, and response to security incidents that might otherwise lead to cyberattacks.
ISPM consolidates and correlates identity-security data, reducing the volume of labor-intensive security alerts and notifications generated by disparate security tools, and paving the way toward more actionable insights and better security decision-making.
Organizations also face difficulties in scaling their security capabilities to meet the evolving threat landscape, especially when relying on manual or siloed security solutions. ISPM offers a scalable and integrated approach to security management, allowing organizations to centralize control and automation to enhance their overall security posture and adapt to new challenges.
ISPM implementation and best practices
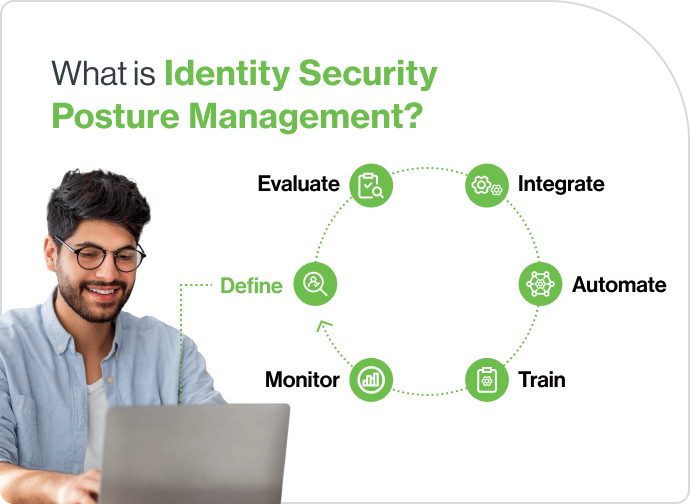
Successful implementation of an ISPM framework requires a thoughtful, strategic approach that begins with thorough — and ongoing — assessment of the organization’s security posture in general and its identity security posture in particular. With that baseline intelligence in hand, the organization can move through the following steps toward ISPM success:
Define security and compliance requirements - Establish clear security objectives and regulatory compliance needs, such as least-privilege access, role-based access control (RBAC), and adherence to industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Evaluate and select ISPM solutions - Research and evaluate ISPM vendors based on your organization's specific needs. Ensure the solution provides integration with existing IAM systems, user behavior analytics, privileged access management (PAM), and threat detection capabilities.
Integrate with existing identity infrastructure - Deploy the ISPM solution and integrate it with your current IAM, cloud environments, and on-premises systems. Ensure compatibility with tools like multi-factor authentication (MFA), identity governance, and privileged access management.
Establish identity security policies and automation - Define and implement security policies within the ISPM solution, such as role definitions, access certification workflows, and automated alerts for risky behaviors or misconfigurations.
Train teams and establish best practices - Provide training for IT and security teams on how to use the ISPM solution, respond to alerts, and follow identity security best practices. Ensure ongoing education to adapt to new threats and changes in identity management.
Monitor and remediate identity risks - Use the ISPM solution to continuously monitor identities, permissions, and access activities in real-time. Actively remediate risks like excessive privileges, unauthorized access, and non-compliance through automation or manual interventions.
Continually evaluate and improve - Regularly review the effectiveness of the ISPM solution through audits, access reviews, and updates to security policies. Adjust and scale the solution as your organization grows or new compliance requirements emerge.
Following these steps, your organization can effectively adopt and maintain a robust ISPM solution to secure its identity and access landscape.
The future of ISPM
Safeguarding digital identities will see significant advancements and innovations in the very near future. As cyber threats continue to evolve and grow in sophistication, the need for robust and proactive identity security measures becomes even more critical. Technology vendors are answering that call with ID security innovations that include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for robust behavioral analysis and advanced threat detection and response.
IPSM is poised to benefit from these trends as it grows to encompass a wider range of tools and capabilities. It will evolve to integrate more aspects of security management, including identity and access management, security information and event management (SIEM), and cloud security, providing organizations with a comprehensive and unified platform for enhancing their ID security posture.
The next generation of ISPM capabilities will feature more personalized and adaptive security measures that eschew static rules and policies and focus more on AI- and ML-enabled systems for adaptive, context-aware controls that respond to individual user behaviors and security incidents in real-time.
Access Management
Access management combines tools and policy controls to ensure only the right users have access to applications and resources and under the right conditions. Duo’s access management solutions integrate with major systems like Active Directory to deliver multi-factor authentication (MFA), passwordless authentication, and single sign-on (SSO) capabilities to verify user identities and enforce role-based access. They protect critical resources from stolen credentials and unauthorized access that can lead to systems compromise and data loss.
PRODUCTDevice Trust
Identify risky devices, enforce contextual access policies, and report on device health using an agentless approach or by integrating with your device management tools. Duo Device Trust delivers visibility, health posture, and continuous endpoint verification to help reduce risk and enforce policies on any device, anytime, anywhere.
SOLUTIONPhishing Prevention
Phishing attacks are a common security threat designed to steal sensitive information like login credentials and financial data. It’s the No. 1 cause of security breaches — but despite their notoriety, phishing campaigns continue to plague even the most vigilant defenders. Duo provides a critical foundation for a Zero Trust security strategy coupled with phishing-resistant MFA to verify users truly are who they say they are.
